What is the Ethereum Pectra Upgrade?
Ethereum’s evolution never stops. The incoming Pectra upgrade is a major milestone in the entire history of the Ethereum network.
The upgrade aims to improve the overall efficiency and functionality of the network. It focuses on the numerous Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), specifically the EIP-3074, scheduled to go live in Q1 of 2025.
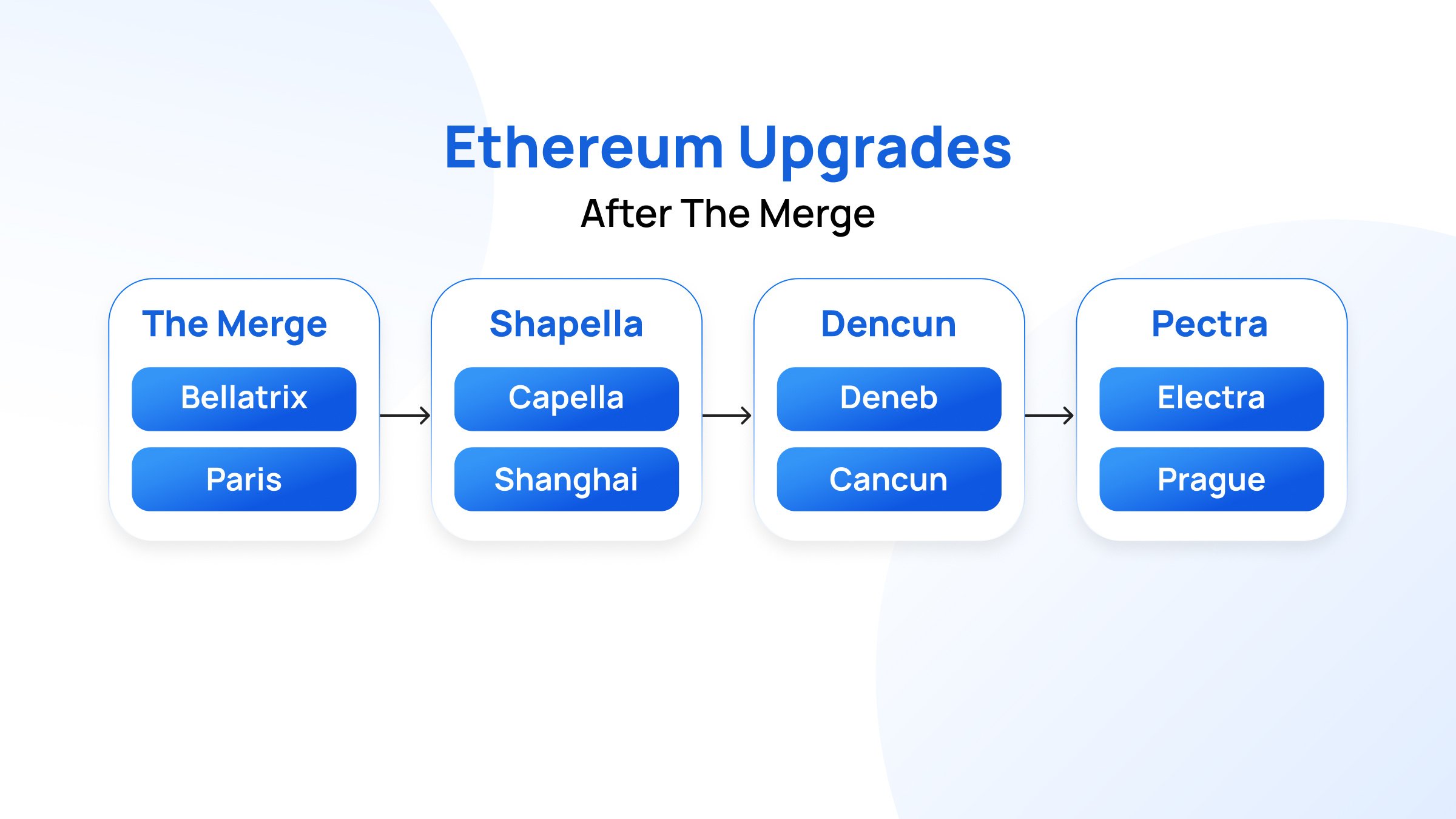
Specifically, the Pectra Upgrade follows the recent success of the Ethereum Dencun upgrade.
The upgrade enhances how Ethereum handles transactions through smart contracts and improves wallet usage capabilities on top of the network.
The EIP-3074 proposal includes capabilities like grouped transactions, which enable users to sign in to a transaction only once without considering the number of tasks it contains.
Additionally, this upgrade intends to simplify the network’s functions while amplifying users' experiences on Ethereum. It also seeks to curb the network’s high transaction expenses and complexities holistically. The EIP-3074 comes with a new feature dubbed “social recovery,” which allows users to regain access to their assets in their crypto wallets without the need for seed phrases.
What that sounds impressive, it doesn’t end there.
The upcoming Pectra upgrade is also a key part of the Ethereum network’s future-proof plan. By achieving this, Ethereum will strengthen how it classifies itself as one of the leading decentralized application (dApp) and smart contract platforms, taking the blockchain industry to the next level.
A Closer Look at the Security Implications of EIP-3074
As we dive deeper into the breakdown of the Ethereum Pectra Upgrade, it’s important to know some of the key security implications brought by the EIP-3074 proposal introduction.
Needed for Trusted Invokers
EIP-3074 allows Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) to delegate transaction signing to a designated smart contract (the "invoker").
The Ethereum network developers are expected to include mechanisms like whitelists to enable only confirmed users to participate in transactions on the network.
If this invoker contract is compromised (e.g., due to a vulnerability), it could lead to the loss of all assets associated with the EOA. This is a much higher risk compared to traditional EOAs, where a single compromised transaction typically affects only the funds involved in that transaction.
Replay Attacks
EIP-3074 transactions are susceptible to replay attacks if not adequately protected.
An attacker could intercept and re-broadcast a valid transaction, potentially leading to unauthorized actions and financial losses.
Implementing robust replay protection mechanisms, such as nonces or timestamps, is essential.
Invoker Contract Vulnerabilities
The security of the EIP-3074 system heavily relies on the invoker contract's implementation.
Any vulnerabilities in the invoker contract, such as reentrancy bugs or logic errors, could be exploited to drain funds or manipulate transactions.
Thorough audits and security reviews of invoker contracts are paramount.
Other Ethereum Pectra Upgrade EIPs
To strike a balance uniformly, the upgrade is not centered only on the EIP-3074, but it envisions moving a step forward to bring deeper, more significant changes through the other available Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), aimed at improving the protocol’s efficiency while future-proofing the blockchain alongside. This extensively includes both retroactive EIPs that clarify both existing and new protocols and proposals.
Here are some key EIPs included in the Pectra Upgrade and their functions:
- EIP 7523: This proposal type ensures future upgrade compatibility and limits smart contract creation to addresses. It strives to also ensure the efficiency of the Ethereum network by removing empty accounts from the Ethereum state, which helps reduce the state’s size, making the network scale faster and easier to use.
- EIP-2537: The EIP-2537 enhances the operation of the BLS12-381 curve by introducing new pre-built functions. This helps make cryptographic processes more efficient for everyone. The more cryptography, the better security verification on the network is ensured.
- EIP-5920 (Pay opcode): As the name suggests, this EIP proposal also functions to improve the Ethereum network's scalability. It enables users to share ETH directly with one another without the need to activate the receiver’s contract code.
- EIP-7610: This EIP prevents account overwriting with the fork on the network. The system does not permit users who try to make an account post-Pectra in a place where there’s already an account. It’s designed for the system to be susceptible to future upgrades, mainly via Verkle trees.
- EIP-3074, 5806, and 7377: These additions are account abstraction EIPs that speed up the network transaction process. The EIP-3074 brings new commands called AUTH and AUTHCALL. These are opcodes that enable transaction contracts to be verified and executed more autonomously whenever certain permissions are set.
- EIP-7251 (Maxeb): It’s designed to make the Ethereum network more scalable and simplify validator management. It does this by increasing the maximum effective balance for validators from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH on the network.
Vitalik Buterin Drafts EIP-7702 in 22 Minutes!
Adding to the aforementioned EIPs, the latest one introduced by Ethereum’s Vitalik Buterin to support network transaction scaling is EIP-7702.
Characterized as one of the most impactful changes on the Ethereum blockchain, the introduction of EIP-7702 left the Ethereum community amazed. It came as the next big network proposal to support the Pectra upgrade.
This proposal introduces a new transaction type designed to enhance Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs), providing an alternative to the previously discussed EIP-3074.
After the release of EIP-3074, some of the Ethereum community praised the proposal. Others also expressed their displeasure and what they thought about the EIP. The majority of the concerns raised by some members of the community were centered around how the EIP was not compatible with the earlier ERC-4437.
Key Features of EIP-7702
- Temporary Smart Contract Conversion: EOAs are temporarily converted into smart contract wallets during transaction execution, unlocking additional functionalities without permanently altering their nature.
- Transaction Batching: Multiple transactions can be bundled together, increasing efficiency and potentially reducing gas fees.
- Fee Sponsorship: Transactions can be paid for by another account, benefiting users with limited resources or those seeking sponsored interactions.
- Wallet Privileges: The proposal outlines mechanisms for managing wallet privileges, including the ability to grant limited permissions to specific subkeys. This enhances security by allowing users to control access to different assets or functions within their wallet.
Comparison to EIP-3074
While EIP-3074 also aimed to enhance EOAs by enabling features like transaction sponsorship, EIP-7702 takes a different approach by temporarily converting EOAs into smart contract wallets.
This may address some of the security concerns associated with EIP-3074, as it avoids the need for permanent delegation of transaction signing authority.
What is Account Abstraction (AA)?
The concept of account abstraction (AA) is simple, and EIP-7702 brings it much closer to reality.
The Ethereum ecosystem has two types of accounts:
- externally owned accounts (EOAs), and
- contract accounts.
EOA functionalities depend on private keys to execute transactions, while contract accounts are controlled by code.
Account abstraction makes distinctions between these accounts based on how they operate. Account abstraction treats all accounts on the Ethereum blockchain as contract accounts. This allows EOAs to be replaced by smart contract wallets, which have arbitrary logic to validate transactions.
What Should Users Look Out for After the Pectra Upgrade (Hard Fork)?
There are more streamlined upgrades revealed by the Ethereum developers to take place after the upcoming debut of the Pectra upgrade. Although the developers never mentioned the actual release date of the pending upgrades, this means that after Pectra, the Ethereum community should expect more updates in the ecosystem.
Apart from the Pectra upgrade, many believe that Verkle trees should be the next upgrade on the Ethereum blockchain. The introduction of the Verkle trees will upgrade the Ethereum nodes to validate blocks without the need to store a large amount of state data on the blockchain.
Furthermore, the upgrade will bring Ethereum a step forward towards statelessness. When this is achieved, there will be no need for a stateless client to store a whole database to validate blocks on the network.
Closing Thought
Ethereum's long-standing aim to solve the trilemma of blockchain and make the technology more efficient to use in our daily lives has been well-felt. From migrating from a Proof of Work (PoW) to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, Ethereum network upgrade evolution never stops.
Solving the network’s scalability crisis will allow more investors and traders to flock to the network, thereby increasing the blockchain’s user-based.
The upcoming Pectra hard fork aims to improve how users transact on the network and manage their crypto wallet.
Safety, efficiency, and uprated features are some of the major advantages that will be provided to users by the arrival of the EIP-3074 proposal.
