In traditional finance, verifying transactions is straightforward. When a person makes a transaction, it is immediately reflected in the account statements of both the sender and receiver, allowing for easy verification. But, in blockchain systems and cryptocurrencies, this process isn't as intuitive due to the decentralized and pseudonymous nature of these technologies.
Despite the complexity, blockchains are lauded for their transparency and the public availability of transaction data. This raises a critical question: how can an average person verify a transaction on a blockchain?
For instance, if you send cryptocurrency to another address, how can you confirm the transaction was successful and ensure the funds reached the correct recipient? Further, in the case of smart contract interactions, verification becomes even more crucial, particularly when auditing transactions or recovering from errors like sending funds to the wrong contract.
To address these needs, we require a sophisticated yet user-friendly interface capable of displaying blockchain transactions in an accessible and straightforward manner.
This is where blockchain explorers come into play.
Blockchain explorers provide a transparent window into blockchain activities, allowing anyone to track and verify transactions, explore wallet addresses, and gain insights into the workings of smart contracts.
In this article, we will clearly explain what blockchain explorers are, how they work, and how you can use them as part of your crypto journey.
What Is A Block Explorer (a.k.a. Blockchain Explorer)?
A blockchain explorer (a.k.a. block explorer) is a tool that allows you to view and search the contents of a public blockchain. It provides a user-friendly interface to access details about transactions, wallet addresses, and blocks, making the complex blockchain data transparent and easily understandable.
Think of it as a search engine for exploring the blockchain.
While the blockchain itself contains a wealth of information, it is not easily interpretable in its raw form. This is where the block explorer comes in.
A blockchain explorer aggregates, organizes, and presents the data in a user-friendly format, allowing users to search for specific transactions, addresses, or blocks.
You can trace the journey of a single Bitcoin (or any other cryptocurrency) from its inception, see the balance of any given wallet address, and verify the status of a pending transaction.
The first blockchain explorer was made available in November of 2010 for Bitcoin at theymos.ath.cx:64150/bbe.
Many different explorers, each tailored to a specific blockchain, vary in their features and capabilities. However, their core function remains the same: to provide a transparent and accessible view of the complex world of blockchain data.
As for the interface, most explorers will have the following sections:
- Search Bar: Allows you to enter transaction IDs, wallet addresses, block numbers, or smart contract addresses.
- Navigation Menu: Provides links to different sections such as transactions, blocks, addresses, smart contracts, and network statistics.
- Real-Time Updates: Displays the latest blocks and transactions being added to the blockchain.
The image shown above is a screenshot of the Bitcoin blockchain explorer from Blockchain.com.
- The Red box shows the “Search Bar”
- The Green box shows the “Navigation Menu”
- The Blue box shows the “Real-Time Updates”
Why Is A Block Explorer Useful For The Everyday User?
For the everyday crypto user, a blockchain explorer serves several purposes. It provides transparency by allowing you to verify the details of your own transactions. If you're sending or receiving crypto, you can track the progress of your funds in real-time.
Additionally, explorers can help you research the history of a particular token or address before investing, giving you insights into its past activity and potential risks.
For developers and researchers, blockchain explorers are invaluable tools for analyzing trends, identifying patterns, and understanding the overall health of a blockchain network. They provide a wealth of data that can be used to assess network activity, transaction volume, and other key metrics.
While most blockchain explorers have overlapping features and similarities, they are still different products at the end of the day. Below are links to a few useful guides on some of the best blockchain explorers currently in use:
- What Is Etherscan And How To Use It?
- What Is Solscan And How To Use It?
- What Is BscScan And How To Use It?
- What Is TRONSCAN And How To Use It?
How To Use A Blockchain Explorer? Use Cases Explained
Using a blockchain explorer is relatively simple:
- Search Bar: Enter a transaction ID, wallet address, block number, or smart contract address into the search bar.
- Browse Results: Navigate through the detailed results that provide comprehensive data about your query.
- Analyze Data: Use the provided data to verify transactions, monitor wallet activity, or audit smart contract interactions.
Blockchain explorers offer a wide range of functionalities for various use cases. Some of them are listed below:
- Transaction verification
- Address analysis
- Block exploration
- Smart contract interaction
- Analytics and research
Let’s quickly cover each of them and then (in the next section) look at some everyday scenarios where blockchain explorers come in handy.
Transaction Verification
- Hash Search: Users can input a transaction hash (a unique identifier) into the explorer's search bar to retrieve detailed information about a specific transaction, including sender and receiver addresses, amount transferred, transaction fee, and timestamp.
- Mempool Analysis: Explorers can display pending transactions in the mempool (the waiting area for transactions before they are included in a block), allowing users to estimate transaction confirmation times.
Address Analysis
- Balance Check: Explorers show the balance of a given wallet address in the native cryptocurrency or tokens.
- Transaction History: They provide a chronological list of all transactions associated with an address, revealing its activity patterns.
- Token Holdings: For blockchains supporting tokens (e.g., Ethereum), explorers can display the types and amounts of tokens held in a wallet.
Block Exploration
- Block Details: Users can search for a specific block by its height or hash and view its contents, including the list of transactions, miner address, timestamp, and difficulty.
- Chain Statistics: Explorers often present real-time data on block height, network hash rate, average block time, and other network metrics.
Smart Contract Interaction (Ethereum and Similar Blockchains)
- Contract Source Code: Explorers can display the source code of deployed smart contracts, allowing developers to audit and verify their functionality.
- Read/Write Functions: Users can interact with smart contracts through the explorer's UI, invoking read functions to query data or write functions to execute transactions.
Using Block Explorers In Your Day-To-Day Transactions: Top 8 Scenarios
1. Checking Transaction Status
After sending cryptocurrency to someone, you can use a blockchain explorer to verify that the transaction has been successfully processed and confirmed on the blockchain. This is essential for ensuring that your funds have reached their destination.
2. Verifying Received Payments
If you're expecting to receive cryptocurrency, you can use an explorer to check whether the payment has been sent and to see the transaction details, including the sender's address and the amount.
3. Checking Wallet Balance
You can easily check the balance of your cryptocurrency wallet by simply entering your wallet address into a blockchain explorer. This is a convenient way to keep track of your holdings.
4. Investigating Suspicious Activity
If you notice any unusual activity on your wallet or suspect fraudulent transactions, you can use an explorer to trace the origin of the funds and gather evidence for reporting to authorities.
5. Researching Token Information
Before investing in a new cryptocurrency or token, you can use an explorer to research its history, check its total supply, and see the distribution of tokens among holders.
6. Monitoring Smart Contracts
If you're interacting with a decentralized application (dApp) or using a smart contract, you can use an explorer to view the contract's code, verify its functionality, and monitor its activity.
7. Checking NFT Ownership
For non-fungible tokens (NFTs), you can use an explorer to verify ownership, view the token's metadata (such as images or descriptions), and track its transaction history.
8. Tracking Whale Activity
Some users monitor the transactions of large holders ("whales") to gain insights into market trends and potential price movements. Blockchain explorers make this possible by allowing you to see the transactions of any address.
How Do Blockchain Explorers Work?
Want to dive deeper and understand how block explorers work under the hood? Here’s a detailed explanation for the select few who make it this far!
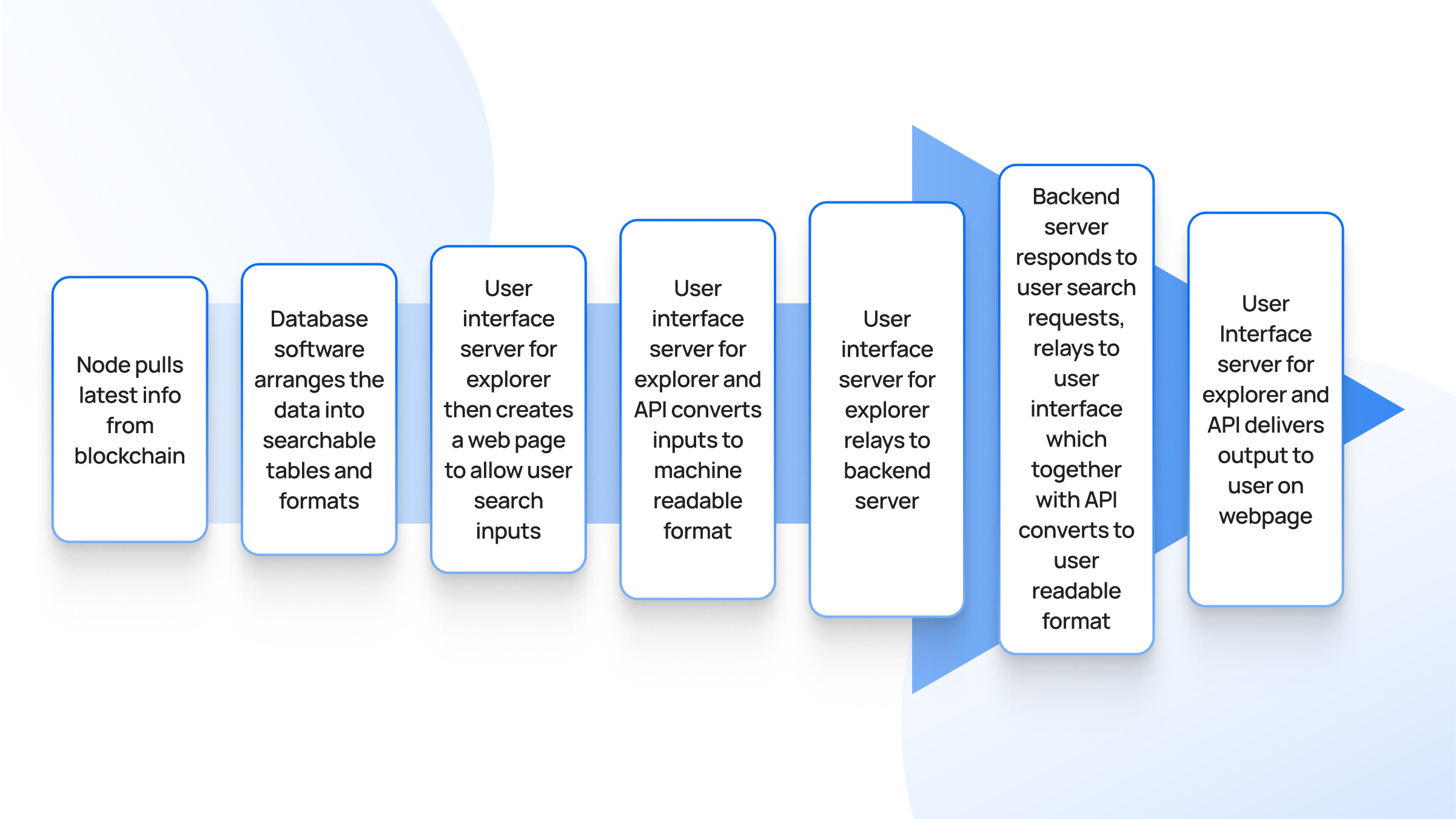
While blockchain explorers may appear simple to end-users, under the hood, they employ a combination of advanced technologies and techniques to retrieve, process, and present blockchain data in a user-friendly manner.
1. Node Synchronization
A blockchain explorer begins by running a full node of the respective blockchain network (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). This node continuously pulls the latest information from the blockchain, ensuring it stays synchronized with the network.
The node validates and stores all blocks and transactions according to the consensus rules of the blockchain protocol.
- Key Components: Full Node Software (e.g., Bitcoin Core, Geth)
- Function: Downloading and validating the entire blockchain to ensure data integrity and authenticity.
2. Data Extraction and Database Management
Once the full node is synchronized with the blockchain, specialized software (often referred to as indexers) extracts relevant data from the blockchain and organizes it into a structured database.
This involves parsing blockchain data into tables that can be efficiently queried.
- Key Components: Indexers, Database Management System (DBMS)
- Function: Transforming raw blockchain data into structured, indexed tables for fast retrieval.
3. User Interface (UI) Server Setup
The UI server for the blockchain explorer creates web pages that allow users to input queries and interact with the explorer.
This involves designing and deploying a front-end interface that can accept various types of user inputs (e.g., transaction IDs, block numbers, wallet addresses).
- Key Components: Web Servers, Front-End Frameworks (e.g., React, Angular)
- Function: Providing an intuitive interface for users to interact with blockchain data.
4. Input Conversion and API Handling
The user inputs are converted into machine-readable formats using APIs. The UI server and the API layer together translate user requests into specific instructions that the backend can process.
- Key Components: API Gateways, RESTful Services, GraphQL
- Function: Converting user-friendly queries into backend requests.
5. Backend Query Processing
The backend server receives the converted queries and performs the necessary database operations to retrieve the requested information. This server communicates with the database where the indexed blockchain data is stored.
- Key Components: Backend Frameworks (e.g., Node.js, Django), Database Query Engines
- Function: Executing queries on the structured blockchain data to fetch results.
6. Response Handling and Formatting
Once the backend server retrieves the required data, it sends the information back to the UI server.
The UI server and API layer then convert the raw data into a user-readable format. This often involves formatting the data into tables, charts, or other visual elements.
- Key Components: Data Formatting Libraries, Serialization (e.g., JSON, XML)
- Function: Converting raw query results into a format suitable for display.
7. Output Delivery to Users
The formatted data is delivered to the user through the web interface. The explorer presents the information in an accessible and comprehensible manner, allowing users to analyze the blockchain data effectively.
- Key Components: Front-End Rendering, Web Browsers
- Function: Displaying the formatted data to users on the web page.
Technical Architecture of Blockchain Explorers
Component |
Functions |
|
Full node |
|
|
Indexer |
|
|
Database |
|
|
UI server |
|
|
API layer |
|
|
Backend server |
|
|
Front-end display |
|
Examples Of Top Block Explorers For Different Blockchains
Blockchains |
Explorers |
|
Bitcoin |
Blockchain.com Explorer, Blockchair, BlockCypher |
|
Ethereum |
Etherscan, BlockScout, Ethplorer |
|
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) |
BscScan, Bitquery |
|
Solana |
Solscan, Solanabeach, Solblock |
|
Tron |
Tronscan, TRON Grid |
|
Polygon (Matic) |
Polygonscan, Matic.network Explorer |
|
Avalanche |
Snowtrace, Avascan |
|
Cardano |
Cardanoscan, Cexplorer |
|
Polkadot |
Subscan, Polkascan |
|
Cosmos |
Mintscan, Big Dipper |
Conclusion
Blockchain explorers are vital tools for everyone in the cryptocurrency space. They act as a real-time visual validation for most users’ transactions, which is particularly crucial when there is no intermediary between a transaction to troubleshoot or catch the losses.

