A dApp, or decentralized application, is a software application that operates on a decentralized system, utilizing a large number of nodes rather than a single centralized server.
According to DappRadar’s dApp Industry Report, Unique Active Wallets (UAWs) have experienced a 124% year-over-year (YoY) growth rate, with an average of around 4.2 million UAWs daily in 2023.
Additionally, the transaction count in the DeFi sector crossed 5 billion, with an over 537% YoY surge.
_%20A%20Beginner%E2%80%99s%20Handbook-2.jpg)
Apart from DeFi, sectors such as gaming, NFTs, social, and others contributed almost 14 billion transactions in 2023 compared to the 10 billion total transactions in 2022. These figures indicate the increased demand and associated growth in the dApp space.
In this article, we’ll see what decentralized applications (dApps) are, how they work, and how you can get started with them.
What Is A DApp?
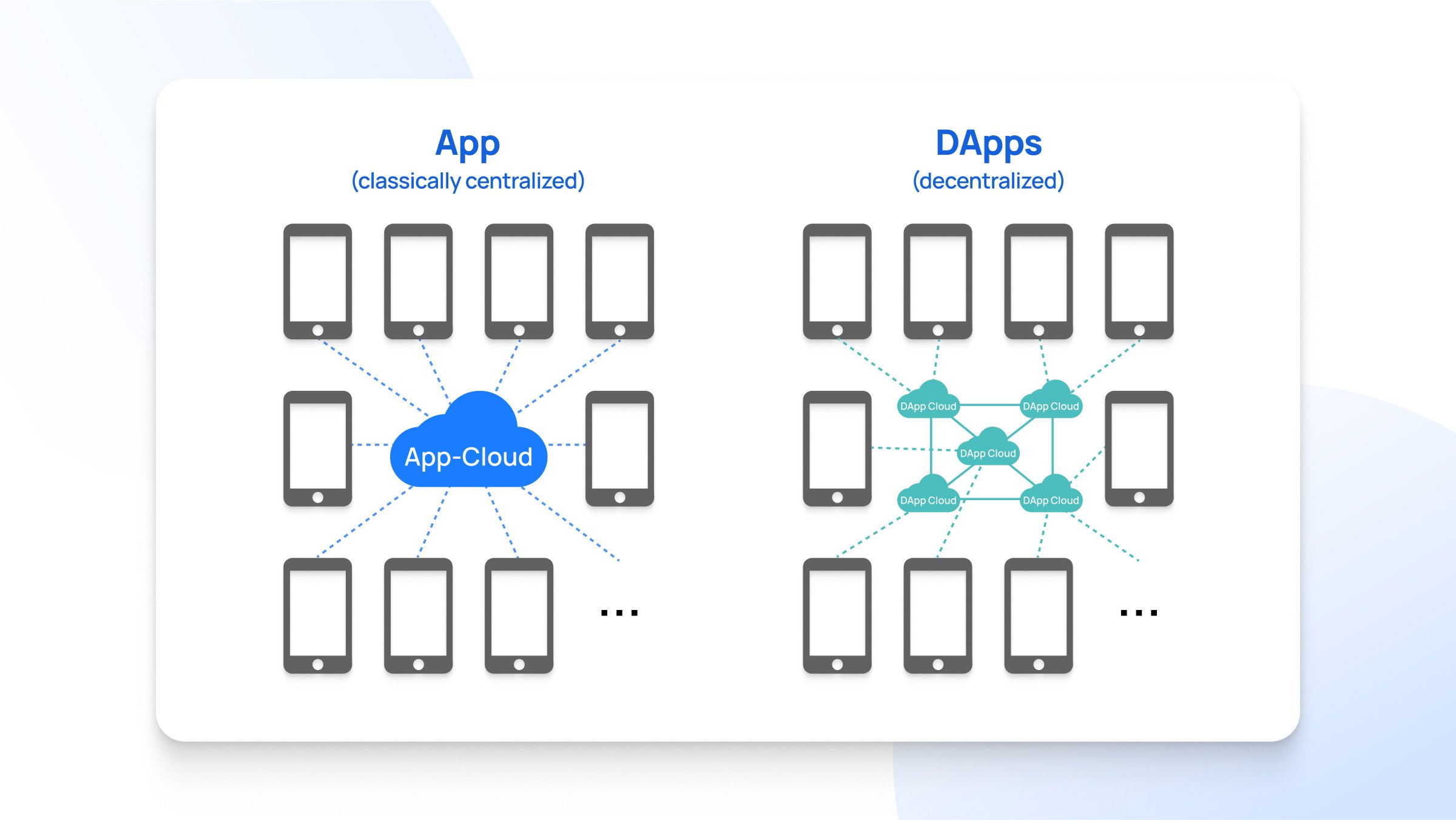
A dApp is an open-source software application that operates on a peer-to-peer network, typically a blockchain. In a blockchain ecosystem, a dApp can be oversimplified as a smart contract with a human-readable UI.
Based on a document published as ‘The General Theory of Decentralized Applications, Dapps’ by technologist David Johnston and others, an application must fulfill the following criteria to qualify as a dApp.
- An application must be open-source and operate autonomously without any entity controlling its token supply’s majority.
- As a measure to avoid central points of failure, the application data and its operational records must be cryptographically stored in a decentralized public blockchain.
- It’s mandatory to use a cryptographic token that facilitates access to the application and to reward miners or yield farmers.
- An application's token generation must function based on a consensus mechanism such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Proof of Work (PoW).
How Do DApps Work?
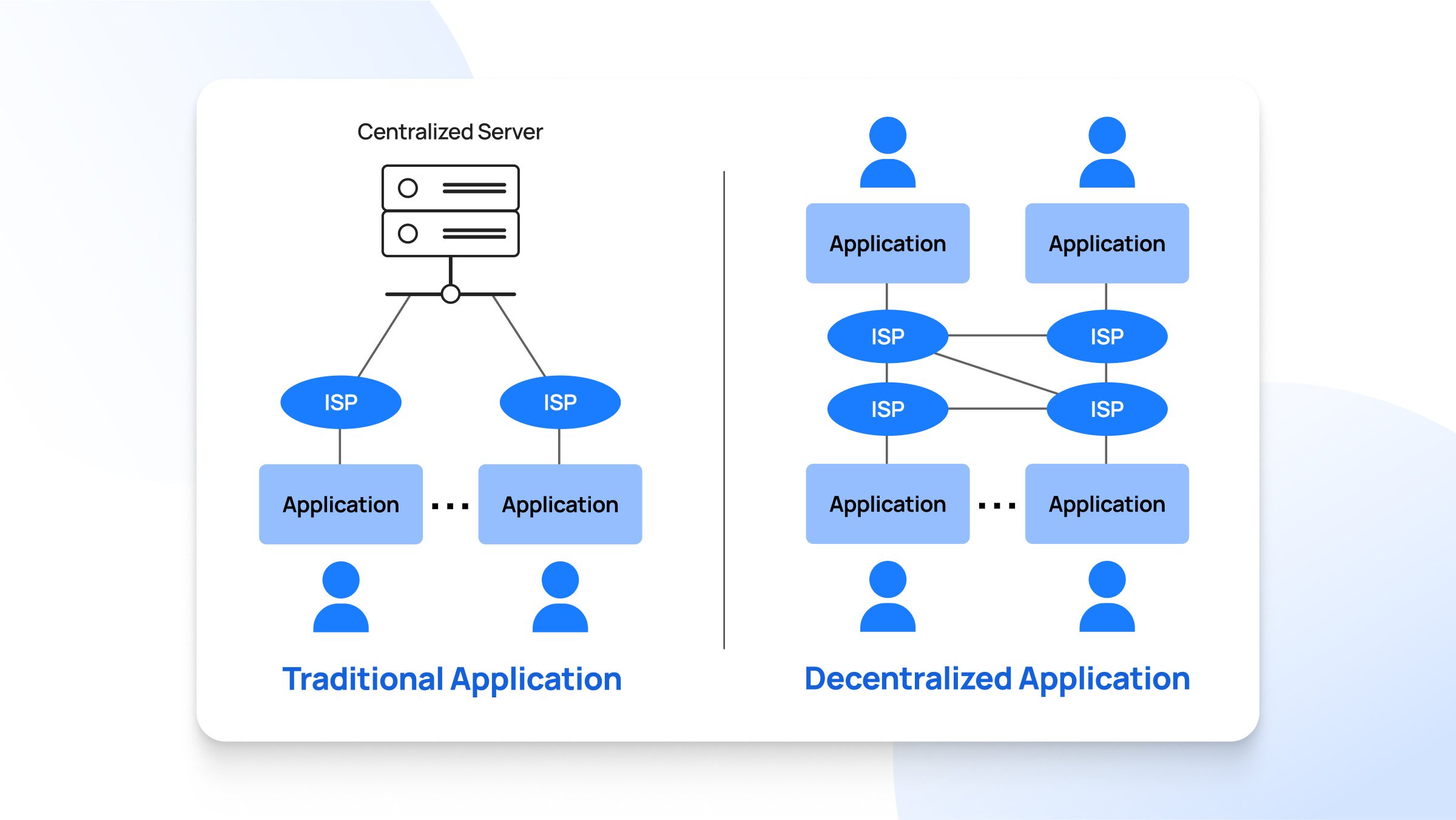
A dApp is (generally) built on a decentralized public network with a user interface (UI) that allows the crypto community to participate in various activities such as payment, token transfer, NFT purchase, exploring the metaverse, staking, and more.
To ensure a smooth and efficient user experience, the dApp’s backend is powered by smart contracts, which facilitate decentralized decision-making and transparent operations. The smart contracts deployed can be simple or complex, depending on the dApp's desired functionality.
The four major components that help in the proper functioning of decentralized applications include the following:
- Smart contracts
- Cryptocurrency
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
- Oracle
1. Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a self-executing program on a blockchain that functions strictly based on the provided set of instructions. The involvement of smart contracts eliminates the need for a central authority to enforce an agreement or a contract.
Developers custom program the smart contract to ensure that their dApp provides the desired crypto services to its users in a secure, transparent, and automated manner.
2. Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency can be considered as the lifeblood of dApps as it serves as the primary medium of exchange. Participants use various supported cryptocurrencies to pay fees, buy or mint NFTs, purchase in-game items, and more.
In addition to spending, dApp users are also rewarded with cryptocurrencies for participating in various activities such as gaming, staking, liquidity provision, and yield farming.
3. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is the foundation upon which blockchains are built. It records the transactions of digital assets, and all the transactional details are stored in multiple nodes. DLT's involvement helps avoid the central point of failure and adds transparency.
In short, DLT allows dApps to operate efficiently, securely, and transparently without the support of any central authority and their centralized servers.
4. Oracle
Blockchains innately lack the potential to connect and acquire real-world data and oracles like Chainlink supply the required off-chain data on a real-time basis. For example, Oracle on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) provides its users with the live price of cryptocurrencies to help execute transactional activities.
Oracle's involvement is crucial for the proper function of dApps that provide services on decentralized finance (DeFi), NFT marketplace, supply chain services, and other sectors requiring real-time off-chain data.
Major Features of Decentralized Apps (DApps)
Accessibility
Decentralized applications allow you to access and use various crypto-based services regardless of your physical location. For example, in the case of DeFi, dApps open the door for a wide range of decentralized platforms for trading, staking, investing, etc., boosting financial inclusion due to their low entry barrier.
Transparency
The public availability of blockchain transactions using free online tools like block explorer helps you analyze in-depth details of your transactional activities. This transparency helps to reduce the chance of potential fraud or illegal activities that might result in the loss of users' crypto assets.
Security
The data stored on the blockchain is highly secured using complex cryptographic algorithms to restrict the possibility of data alteration, tampering, or deletion. The operation of dApp on the blockchain network also minimizes the chances of a single point of failure and resists attacks even if a few individual nodes are compromised.
Cost-Effective
The absence of intermediaries like financial institutions allows dApp users to complete their crypto activities for low fees without compromising on transactional speed and efficiency. For example, you can use Solana-supported dApps to enjoy fast and low-cost transactions for a median fee of just $0.00064.
Top Use Cases of Decentralized Applications (DApps)
With the help of dApps, users can seamlessly interact with various major sectors, such as:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi aims to provide a decentralized alternative to the existing financial services offered by banks and other similar institutions.
The availability of dApp unlocks the potential of faster crypto activities with zero brokerages and a reduced fee structure, allowing users to participate in trading, investing, lending, borrowing, staking, yield farming, and more.
Supply Chain Management
In the case of supply chains, dApps leverage blockchain technology so that users can obtain extensive information related to the product journey in real-time.
The availability of this live tracking facility induces transparency between the customer and suppliers, which in turn builds trust and reliability within the supply chain management ecosystem.
Gaming
Decentralized gaming facilitated by dApps allows global gamers to create a strong community and participate in online competitions to win prizes, including cryptocurrencies, NFTs, etc.
Popular crypto gaming platforms also reward their users for their participation, which can be converted to assets with real-world value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DApps
Advantages of DApps
- Data Privacy: The absence of centralized data storage helps dApp users preserve the confidentiality of information while accessing or interacting with other platforms.
- Zero Downtime: The presence of a decentralized network of nodes worldwide reduces the possibility of network downtime which is common with central authority-based networks.
- Interoperability: The availability of cross-chain dApps allows users to interact with the services across multiple blockchains without the need to switch among various other applications or platforms.
Disadvantages of DApps
- User Experience: The lack of a user-friendly interface in newer dApps can lead to a bad experience, as the quality of user experience typically improves with time and user feedback.
- Smart Contract Vulnerability: Errors in the deployed smart contracts of dApps can lead to exploitation from bad actors that might lead to the loss of the user's funds.
- Network Congestion: Blockchain network congestion can cause delayed computation when numerous transactions are initiated on some dApps at once.
Major DApp Hacks
Despite the decentralized and generally on-chain nature of dApps, they are not immune to exploits. If the underlying smart contract or infrastructure has vulnerabilities, hackers would pounce on the opportunity to exploit it.
Below are three examples of popular dApps getting hacked:
- KyberSwap: The decentralized exchange KyberSwap was hacked in November 2023, leading to a loss of almost $50 million out of its total value locked (TVL) of around $80 million. The attack stole funds mostly in ETH, wETH, and USDC tokens by targeting multiple cross-chain deployments on Arbitrum, Ethereum, and Optimism, highlighting vulnerabilities across these decentralized networks.
- PancakeBunny: This DeFi yield aggregator lost around $45 million following a flash loan attack in May 2021. In this drastic event, the hacker exploited the system’s vulnerability to manipulate the exchange rates and stole over 114,000 WBNB tokens.
- Parity Wallet: A security bug in Parity Wallet led to the loss of 150,000 ETH tokens worth around $30 million in July 2017. Parity Technologies, the company behind the Parity Wallet, failed to notice the vulnerability in its smart contract, which allowed the hacker to gain control over the user’s funds, resulting in a massive loss.
Examples of Notable DApps
- Uniswap: Launched in 2018, Uniswap is a prominent decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the Ethereum blockchain that allows its users to trade, swap, or stake crypto assets. As one of the largest DEX, Uniswap has high liquidity on top cryptocurrencies that facilitate quick transactions with less price slippage.
- Aave: This decentralized crypto platform allows its users to lend and borrow supported crypto assets. Here, the borrowers need to lock their crypto collateral and pay interest that is distributed among the lenders to lock their assets on Aave.
How To Start Using DApps?
By now, you have a fair idea of what a dApp is and how they are the gateway into DeFi. Now, let’s explore how you can start using dApps.
1. Set Up a Crypto Wallet
A wallet is like your bank account for cryptocurrencies. You need it to interact with dApps.
Popular choices include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet
Make sure the wallet supports the blockchain the dApp runs on (e.g., Ethereum, Polygon).
Read this beginner-friendly guide on how to set up a crypto wallet.
2. Get Some Cryptocurrency
You need cryptocurrency to use most dApps. If you are using a dApp that has integrated Transak, then it becomes a breeze.
Transak lets you buy crypto with your credit/debit card or bank transfer, directly inside the dApp. This makes it very beginner-friendly.
3. Connect Your Wallet to the Dapp
Most dApps have a "Connect Wallet" button. Click it and choose your wallet from the list. Authorize the connection.
Do not authorize or connect your wallet to a dApp that you are not familiar with as bad actors can drain your wallet immediately after you connect to a spammy dApp or website.
4. Start Using The DApp
Each dApp is different, but they usually have a user interface to guide you.
Common actions on a dApp would be:
- Sending/receiving cryptocurrency
- Interacting with smart contracts (e.g., swapping tokens, staking, providing liquidity)
- Buying/selling NFTs
Keep Transak in Mind
Transak makes it easier for beginners to get started with dApps by:
- Letting you buy crypto directly within the dApp, saves you the hassle of transferring from an exchange.
- Supporting multiple blockchains and payment methods.
- Integrating seamlessly with many dApps.
Example with Transak One
Imagine a dApp where you can buy NFTs.
Without Transak, you'd need to buy crypto on an exchange, transfer it to your wallet, and then connect to the dApp.
With Transak One:
- You connect your wallet to the dApp.
- When you want to buy an NFT, you click "Buy with Transak."
- You pay with your card or bank transfer.
- The crypto is sent directly to the dApp's smart contract, and you get the NFT.
- It's all done in one smooth flow.
Conclusion
DApps represent a shift in how we interact with digital services and each other.
By leveraging blockchain's inherent properties of transparency, immutability, and decentralization, dApps break down traditional barriers of trust and control. No longer are we reliant on centralized intermediaries to manage our data, finances, or online identities. Instead, dApps empower individuals to take ownership of their digital lives, fostering a new era of self-sovereignty and peer-to-peer interaction.
These applications have the power to reshape industries, democratize access to services, and create entirely new economic models.
Imagine a world where supply chains are transparent and tamper-proof, where artists can directly monetize their creations without intermediaries, and where individuals have complete control over their personal data.
Further, dApps that have Transak’s suite of products integrated within them are at an advantage as they provide users with the most incredible way to onboard into web3 without all the hassle.